USGS Estimates Oil And Gas In Texas' Eagle Ford Group
The Eagle Ford Group of Texas contains estimated means of 8.5 billion barrels of oil, 66 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, and 1.9 billion barrels of natural gas liquids, according to a new assessment by the U.S. Geological Survey. This estimate consists of undiscovered, technically recoverable resources in continuous accumulations.
“Texas is so well-known for its history of oil and gas production that it’s almost synonymous with petroleum,” said Dr. Jim Reilly, USGS Director. “Texas continues to remain in the forefront of our Nation's energy supply chain with remarkable increases in production and reserves due to the revolutionary unconventional techniques used to release previously unrecoverable resources.”
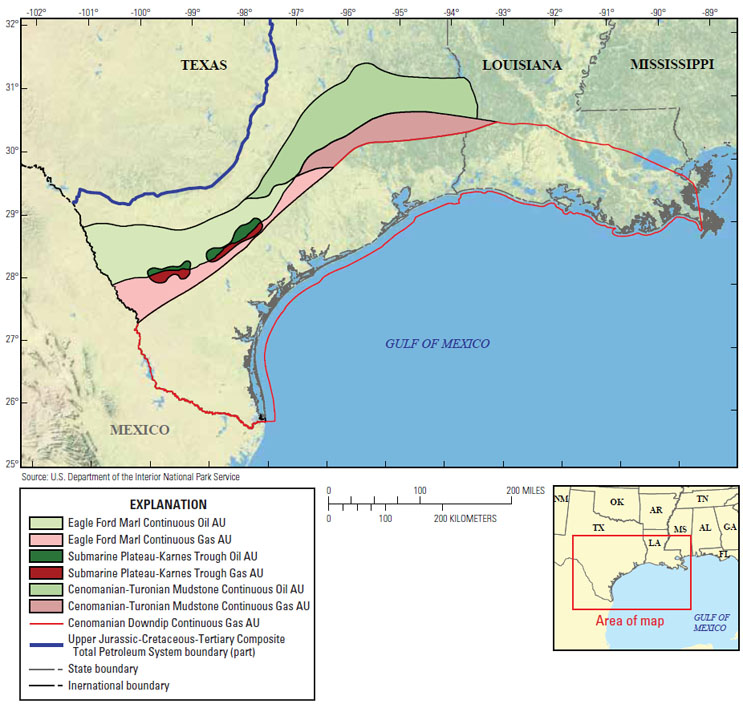
Assessment units of the Eagle Ford Group within the Gulf Coast Basins.
(Public domain.)
The Eagle Ford Group stretches from the Texas-Mexico border to the west, across portions of southern and eastern Texas to the Texas-Louisiana border to the east. It is one of the most prolific continuous accumulations in the United States, and is comprised of mudstone with varying amounts of carbonate.
“The USGS provides value to the Nation by delivering unbiased assessments of U.S. and global energy resources,” said Dr. Reilly. “We regularly reassess potential resources, as we have for the Eagle Ford in this report, in response to changes in estimated ultimate recovery as new techniques or productive horizons are pioneered.”

USGS scientists drilling a research core near Waco, Texas. This core was drilled by USGS during field work for an oil and gas assessment for the Eagle Ford of the Gulf Coast Basins. Cores like these provide information on the various rock layers, such as their make-up, their age, etc.
(Credit: Stan Paxton, USGS. Public domain.)
The Eagle Ford Group has long been known to contain oil and gas, but it was not until 2008 that production of the continuous resources really got underway in East Texas.
“This assessment is a bit different than previous ones, because it ranks in the top five of assessments we’ve done of continuous resources for both oil and gas,” said USGS scientist Kate Whidden, lead author for the assessment. “Usually, formations produce primarily oil or gas, but the Eagle Ford is rich in both.”
Continuous oil and gas is dispersed throughout a geologic formation rather than existing as discrete, localized occurrences, such as those in conventional accumulations. Because of that, continuous resources commonly require special technical drilling and recovery methods, such as hydraulic fracturing.
Undiscovered resources are those that are estimated to exist based on geologic knowledge and statistical analysis of known resources, while technically recoverable resources are those that can be produced using currently available technology and industry practices. Whether or not it is profitable to produce these resources has not been evaluated.

USGS scientists drilling a research core near Waco, Texas. This core was drilled by USGS during field work for an oil and gas assessment for the Eagle Ford of the Gulf Coast Basins. Cores like these provide information on the various rock layers, such as their make-up, their age, etc.
(Credit: Stan Paxton, USGS. Public domain.)
The USGS is the only provider of publicly available estimates of undiscovered technically recoverable oil and gas resources of onshore lands and offshore state waters. The USGS assessment of the Eagle Ford Group was undertaken as part of a nationwide project assessing domestic petroleum basins using standardized methodology and protocol.
The new assessment of the Eagle Ford Formation may be found online. To find out more about USGS energy assessments and other energy research, please visit the USGS Energy Resources Program website, sign up for our Newsletter, and follow us on Twitter.
Source: USGS
