Well Completion
PRODUCTS
-
ABB’s My Measurement Assistant+ is the ultimate digital companion for measurement devices. It leverages Generative AI to streamline maintenance and remote troubleshooting, empowering field technicians and engineers to resolve issues quickly, reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
-
Learn about KROHNE's ultrasonic clamp-on flowmeter for temporary flow measurement of liquids.
-
When using Seeq, teams can easily create automated SPC control charts which can empower data driven decisions.
-
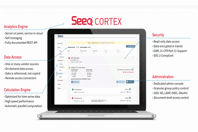
Workbench, Organizer, and Data Lab are powered by Cortex, which enables Seeq calculations at scale, data connectivity, and administration features.
-
ABB’s Sensi+ analyzer offers a reliable new solution which simplifies and reduces the cost of pipeline operation and maintenance. It enables safer, easier, and more efficient pipeline monitoring and operations through a single device that can analyze up to three contaminants (H2S, H2O, CO2) in any natural gas stream accurately and in real time. Its fast response also enables quick reaction to process upsets, thus helping to reduce waste and methane emissions.
WHITE PAPERS AND CASE STUDIES
-
Whether Half-Empty Or Half Full, Krohne Helps Back River Accurately Measure Flow
If a pipe in a wastewater treatment plant is only 50% filled, it doesn't matter whether you call a glass half full or half empty. When it comes to measuring the liquid in that pipe, either way presents a significant problem.
-
How ABB Is Helping Optimize Combustion At Twence's Waste-To-Energy Plant
Maintaining the right level of oxygen is crucial for combustion optimization. Too much excess oxygen equals decreased efficiency. Read more about how ABB is helping Twence optimize combustion in their waste-to-energy plant in the Netherlands.
-
ABB Helps New Zealand's Watercare Comply With New Fluoride Monitoring Regulations
Discover why Watercare, New Zealand's largest water and wastewater utility company, engaged ABB and Water Engineers Limited to install and commission ABB Aztec AFM631 Fluoride Analyzers in their Auckland water treatment plants.
-
Cutting European Methane Emissions Through Advanced Gas Leak Detection
Reducing methane emissions is crucial in combating climate change, and advanced gas leak detection technology is key to achieving this goal.
-
Advances In Online Colorimetric Analyzer Technology
Recent technological developments now enable high-accuracy total phosphorus measurement in near real-time, on-line, that reliably matches lab results.
-
Damper Maintenance Made Easy: ABB's Actuators Minimize Customer Plant Shutdowns
When a customer’s plant stopped working unexpectedly, the ABB team in Brazil stepped up to the challenge.
-
Flow Measurement Of Reservoir Water With A Clamp-On Meter
Discover why clamp-on flow measurement provides a much more reliable and accurate reading compared to other methods.
-
5 Questions To Ask When Selecting An Advanced Analytics Solution
New advanced data analytics have a huge positive impact on the growing volumes of data in many sectors. Learn how to leverage these new analytics in process manufacturing.
-
End-Of-Life Total Flow Alarming System Takes Faulconer Energy To The Edge
FreeWave’s Edge platform with edge polling and alarming future-proofs systems, lowers costs and minimizes operational failures.
-
Not A Drop Of Oil Lost: How Modern Clamp-On Technology Contributes To A Reliable And Cost-Efficient Pipeline Management
Transporting crude oil and petroleum products through pipelines is currently the most efficient way to distribute these energy sources to their respective destinations. To protect the environment and against loss in value due to leakage or theft, systems for leakage detection are required. To ensure safe operation, pipeline management systems must be continuously adapted to the state of the art. Modern and improved ultrasonic clamp-on flow meters offer cost-effective options at this point.
-
Midwestern Utility Takes Data Collection From Manual To Automatic
Read how a publicly owned electric, gas, and water utility taps FreeWave Technologies for new connectivity and edge data collection solution, and achieves immediate, significant results.
-
Building The Digital Oilfield Of The future
Explore how technology is redefining oil field production and data communications.
NEWS
-
Manora Drilling Exceeds Management's Expectations3/9/2026
Valeura Energy Inc. (TSX:VLE, OTCQX:VLERF) (“Valeura” or the “Company”) announces completion of a successful infill drilling campaign at its Gulf of Thailand Manora field (Block G1/48, 70% operated working interest).
-
Viridien Announces Charrua 3D Seismic Survey Offshore Uruguay3/5/2026
Viridien today announced the commencement of the Charrua 3D multi-client survey offshore Uruguay, marking a significant step forward in Uruguay’s offshore energy development.
-
Equinor And Wellesley Launch Joint Exploration Project To Accelerate HPHT Activity On The NCS3/5/2026
Equinor and Wellesley Petroleum have agreed to establish a Joint Exploration Project (JEP) aimed at increasing high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) exploration activity on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (NCS) and contributing to long-term production from existing infrastructure.
-
CanCambria Energy Announces Approval Of Technical Operating Plan For Kiskunhalas Concession Area, Advancing Strategic Oil And Gas Development In Hungary3/5/2026
CanCambria Energy Corp. (“CanCambria” or the “Company”) is pleased to announce that the Hungarian authority responsible for hydrocarbon exploration activities has approved the Company’s technical operating plan for the Kiskunhalas Concession Area (“KCA” or the “Project”), setting forth the commitment and schedule of development activities for the next four years (the “Technical Operating Plan”).
-
Kongsberg Maritime, Seadrill, And Hanwha Drilling Forge Alliance To Pioneer Remote DP Technology3/4/2026
This collaboration represents a shared commitment to defining a global operating model for the future of DP operations for the industry. The initiative will develop the technical and regulatory foundations required for the safe adoption of remote DP and establish a new industry standard.
WELL COMPLETION ABOUT DOCUMENT
Well Completion
Well completion is a process that takes place after a oil or gas well has been verified to be commercially viable. Well completion involves casing, temperature and pressure evaluation and equipment installation to allow gas or oil drilling. Completion therefore has to wait for formation testing after a design well depth has been established. The specific activities involved in well completion include; drill stem tests (DST), production casting, production tubing installation, production flow commencement and installation of beam pumping units.
Drill stem tests have to be conducted to determine production formation potential. The DST experts use appropriate tools lowered into the bottom of the drilling hole to establish the formation potential. Adjustments are made to the tool to establish if the pressure is sufficient for production. This process should be left to the professional crew as hazards such as getting stuck by the test tool in floor testing. Exposure to h2s and other gases as well as blowouts are other hazards that only professional crews know how to deal with.
Production tubing installation is the other process involved in well completion. Small diameter tubing is more preferred to the larger ones in mining. Using couplings, individual tubing is joined to form a tubing string. The tubing that is to be used in mining is made using power tongs. With the advancement in technology, tubing can be made in the form of a continuous coil.
The final step in well completion is the initial production flow. Brine or water is injected into the well to remove the drilling fluid. This should be enough to initiate the flowing of the well. In the event that the well fails to flow under such circumstances, unloading or high pressure gas injection might be necessary. Caution should be taken since blowouts might occur if the well pressures happen to be charged.