USGS Estimates Undiscovered Oil And Gas Resources In The Austin Chalk Formation Of The U.S. Gulf Coast

The Austin Chalk and Tokio and Eutaw Formations of the Gulf Coast Basin contain a mean of 6.9 billion barrels of oil and 41.5 trillion cubic feet of natural gas according to a new assessment by the U.S. Geological Survey. In comparison, the U.S. Energy Information Administration estimates that the United States used 7.5 billion barrels of petroleum products in 2019.
“While the Trump administration continues to develop and expand renewable energy resources, fossil fuels remain a mainstay of the U.S. economy and essential for the continued functioning of industry and in our daily lives. Texas is the state that just keeps on giving when it comes to oil and gas,” said USGS Director Jim Reilly. “Our assessment shows what can be accomplished through advances in technology by industry and the hard work our scientists put in to understanding the geology of petroleum systems in Texas.”
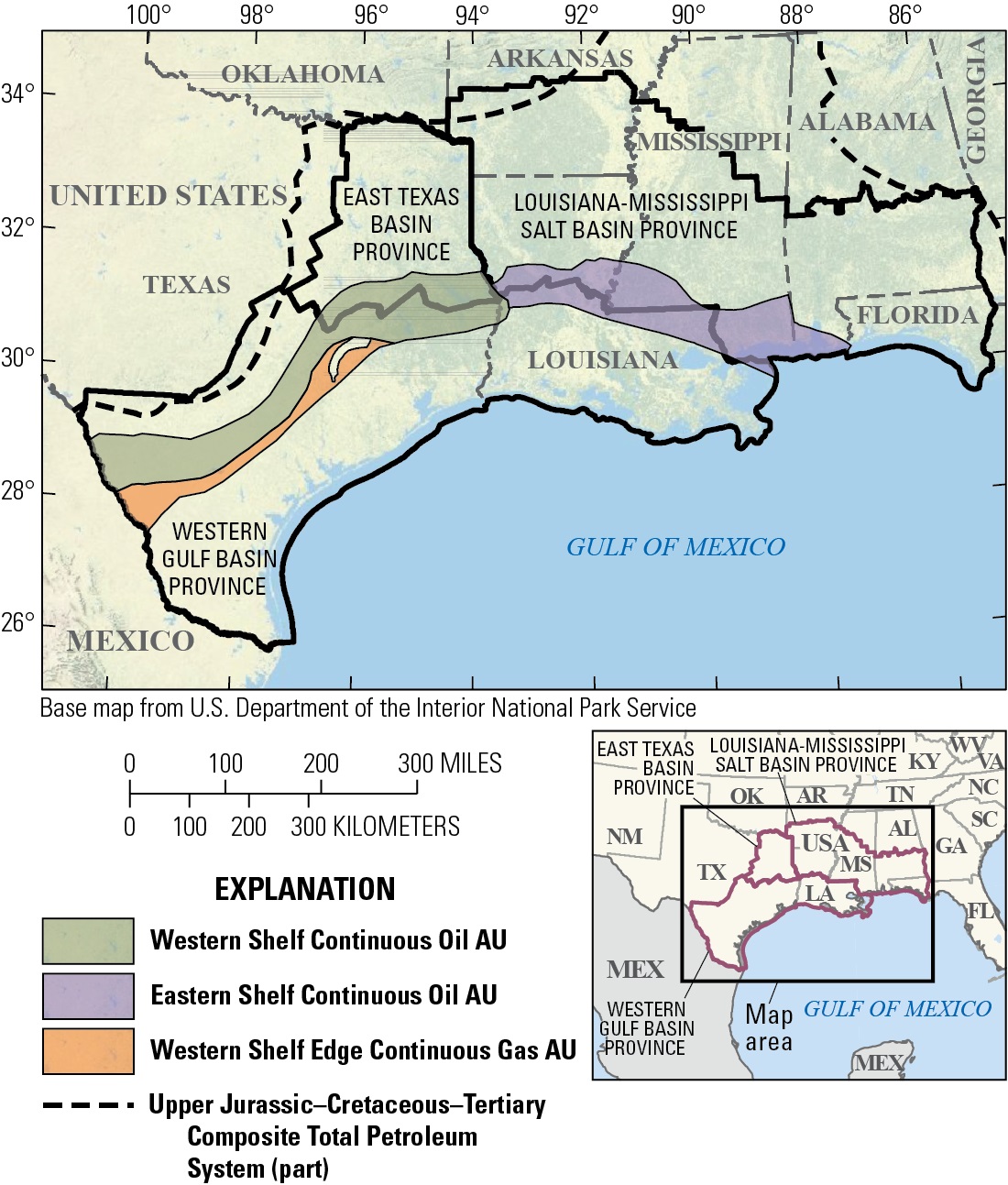
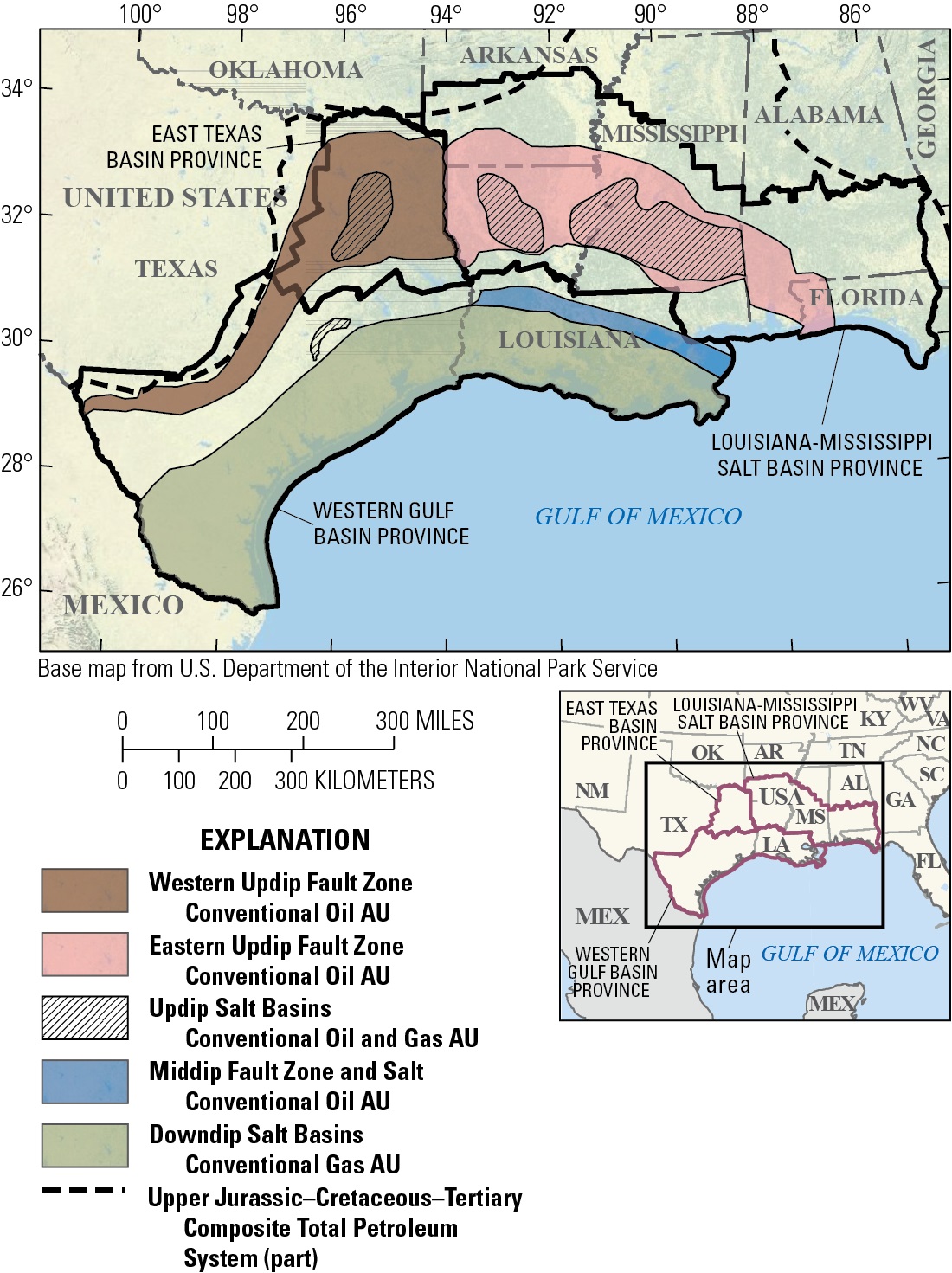
The Austin Chalk and Tokio and Eutaw Formations extend from Texas near the border with Mexico in an arc through Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and into coastal Alabama. Despite covering such a large region, most of the assessed oil and gas resources are in Texas.
These new resource estimates provide an update to the assessment completed in 2010. The update is based on new data, primarily collected through continued drilling, and it accounts for technological advances in resource extraction over the last decade. In addition, USGS scientists and others in the petroleum geosciences have improved their understanding of the underlying geology and petroleum-system elements of the Austin Chalk and Tokio and Eutaw Formations.
The USGS is the only provider of publicly available estimates of undiscovered technically recoverable oil and gas resources of onshore lands and offshore state waters. The USGS assessment of the Austin Chalk was undertaken as part of a nationwide project assessing domestic petroleum basins using standardized methodology and protocol under the Gulf Coast Petroleum Systems and National and Global Assessment of Petroleum Resources Projects.
The assessment provides estimates of both continuous and conventional resources. Continuous oil and gas resources are dispersed throughout a geologic formation rather than occurring as discrete, localized accumulations, such as those in conventional oil and gas fields. Continuous resources require special recovery methods, such as horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing.
This estimate is for undiscovered, technically recoverable petroleum resources. Undiscovered resources are those that are estimated to exist based on geologic knowledge and statistical analysis of known resources. Technically recoverable resources are those that can be produced using currently available technology and industry practices. Whether or not it is profitable to produce these resources has not been evaluated by the USGS.
The new assessment of the Austin Chalk Formation may be found online. To find out more about USGS energy assessments and other energy research, please visit the USGS Energy Resources Program website, and follow us on Twitter.
Source: Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey
